Difference between revisions of "POC Conf. Call 4-26-11"
| (176 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
In attendance: | In attendance: | ||
| − | POC members: | + | POC members: Laurel Cooper (OSU), Ramona Walls (NYBG), Barry Smith (University at Buffalo, NY), Justin Preece (OSU), Justin Elser (OSU), ,Pankaj Jaiswal (OSU), Marie Alejandra Gandolfo (Cornell University) |
| − | Absent: | + | Absent: Dennis Stevenson (NYBG), Chris Mungall (Lawrence Berkeley National Lab), |
| − | Collaborators: | + | Collaborators: none |
| − | Acceptance of the minutes from the [[POC_Conf._Call_4-19-11]]? | + | Acceptance of the minutes from the [[POC_Conf._Call_4-19-11]]? There were no changes, additions or deletions. |
| − | = | + | =Summary of Plant Embryo and Embryonic Plant Structure Terms from last week's meeting:= |
| − | =New terms for | + | ==[http://sourceforge.net/tracker/index.php?func=detail&aid=2982384&group_id=76834&atid=835555 plant embryo (PO:0009009)]== |
| + | |||
| + | Proposed new def'n: A whole plant in the early part of a sporophytic phase after the first cell division. | ||
| + | |||
| + | new proposed comment: An embryo is generally formed after the first division of a zygote, but in the case of adventitious embryos, somatic embryos, other embryos that arise through apogamy, and cultured haploid embryos, it is formed after the division of a single cell that is not a zygote. The end of the embryonic phase varies among taxa. In seed plants, the embryonic phase ends with germination. In pteridophytes, the embryonic phase ends with the formation of the first true leaf after the cotyledon(s). In bryophytes, the embryonic phase ends when the apical cell stops dividing and the sporangium begins to develop. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Add to comment: In cultured plant embryos, the embryonic phase ends when organs (roots, shoot axes, or leaves) begin to form.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''* zygotic plant embryo''' (new term): proposed def'n: A plant embryo that forms as a result of the fusion of gametes. | ||
| + | is_a plant embryo | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''* cultured zygote-derived plant embryo'''(new term): proposed def'n: A zygotic plant embryo that is grown or maintained in culture. | ||
| + | synonym: cultured zygotic embryo, is_a zygotic (plant) embryo, and is_a cultured embryo | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''*microspore-derived''' cultured plant embryo (new term): proposed def'n: A cultured plant embryo that develops from isolated microspores. | ||
| + | |||
| + | is_a cultured plant embryo, synonym: microspore-derived haploid embryo | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''*somatic plant embryo''' (new term): proposed def'n: A plant embryo that forms as a result of apogamy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Comment: Somatic plant embryo may arise where embryos normally would not arise, i.e. on the edges of leaves on Kalanchoe or ferns, | ||
| + | |||
| + | synonym: adventitious embryo (merge into new term) alt id: PO:0004537 | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''*Cultured somatic (plant) embryo''' (PO:0000011) def'n: A (plant) embryo arising from previously differentiated somatic cells in vitro, rather than from fused haploid gametes, i.e., zygote. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''propose revised def'n: A somatic plant embryo arising from previously differentiated somatic cells and grown and maintained in vitro.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''is_a somatic plant embryo and also a cultured plant embryo.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''The above terms and definitions were accepted. Okay to merge adventitious embryo with somatic embryo, but LC will look at it again to make sure.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Need to look for a good examples of somatic plant embryo -- it may be that Kalanchoe does not form embryos before plantlets form, need to check.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''From LC after the meeting:'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''According to George et al , 2008: "Somatic embryogenesis is a process whereby somatic cells differentiate into somatic embryos. Somatic embryos resemble zygotic embryos morphologically. They are bipolar and bear typical embryonic organs. However, they develop via a different pathway. Somatic embryogenesis occurs to a limited extent under natural conditions, within ovules (e.g., Paeonia) and more rarely on leaves (e.g. Asplenium and Kalanchoe)."'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Further evidence of this was presented by Garces et al, 2007, where they showed that constitutive plantlet-forming species, like Kalanchoë daigremontiana, form plantlets by co-opting both organogenesis and embryogenesis programs into leaves. They present evidence of both morphological and gene expression (LEC1 expression ) similarities to the formation of zygotic embryos.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Another example is commonly seen in Citrus, where apomixis occurs - this is perhaps what the original definition of "adventitious embryo" was referring to. (Embryo derived directly from nucellus cells without involving embryo sac cells.) this may be better called "apomitic plant embryo" There is quite a detailed review by Koltunow, from 1993.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''We may want to reconsider merging the adventitious embryo term into the somatic embryo and rather rename it and make it an is_a child of.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Cited Refs:'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''George, E.F., Hall, M.A., and DeKlerk, G.J. (2008). Somatic Embryogenesis. In, The background, Plant propagation by Tissue Culture. Springer SBS, Dordrecht, p. 335–354. (http://www.hos.ufl.edu/mooreweb/tissueculture/february%205/somatic%20embryogenesis.pdf) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Garcês, H. M. P., Champagne, C. E. M., Townsley, B. T., Park, S., Malhó, R., Pedroso, M. C., Harada, J. J., and Sinha, N. R. (2007). Evolution of asexual reproduction in leaves of the genus Kalanchoë. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104, 15578 -15583. | ||
| + | (http://www.pnas.org/content/104/39/15578.full) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Koltunow, A. M. (1993). Apomixis: Embryo Sacs and Embryos Formed without Meiosis or Fertilization in Ovules. The Plant Cell Online, 5, 1425 -1437. | ||
| + | (http://www.plantcell.org/content/5/10/1425.full.pdf)'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''During the meeting PJ posted this link in the chat: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Somatic_Embryogenesis#cite_note-Yang-1 Yang] and sent this by email [[File:20-growth_and_development-02-A.pdf]]'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==[http://sourceforge.net/tracker/index.php?func=detail&aid=3132547&group_id=76834&atid=835555 embryonic plant structures]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | At the [[POC_Conf._Call_4-19-11]] we discussed how to deal with structures that are part of an embryo when the plant is in the embryonic phase but are also part of a plant after it passes out of the embryonic phase, like hypocotyl root junction or coleorhiza. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a solution, we will specify sibling terms like embryonic radicle and seedling radicle, with the correct part_of or participates_in relations and develops from relations (e.g., seedling radicle develops_from embryonic radicle). Includes six classes (see below). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''* embryonic plant structure''' (PO:0025099): Proposed def'n: A plant structure that is part of an embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Comment: Includes plant structures that only occur in embryos (such as suspensor) as well as plant structures that are part of an embryo when a plant is in the embryonic phase (such as embryonic radicle). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''Definition accepted, except should say "plant embryo" instead of "embryo".'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Need to be sure to use "plant embryo" instead of "embryo" in all definitions of descendent terms.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''If, at a later point, we add embryonic phase or specific embryonic phases like 8 cell stage or 16 cell stage, we could use participates_in relation to define embryonic structures. However, as we are now defining it, embryonic plant structures should only include structures that are part of an embryo, not structures that are outside the embryo but present during the embryonic phase (like endosperm).'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Terms that are is_a children of embryonic plant structure:=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''embryo proper''' (PO:0000001): An embryonic plant structure that is the body of a developing embryo attached to the maternal tissue in an ovule by a suspensor. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''scutellum''' (PO:0020110): An embryonic plant structure that is a more or less shield-shaped and absorptive portion of an embryo of Poaceae. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''suspensor''' (PO:0020108): An embryonic plant structure at the base of an embryo that develops from an embryonic basal cell and connects an embryo proper to the wall of a megagametophyte. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | From DWS: We can also use Singh's "Embryology of Gymnosperms" as a basic reference to create a list of terms that are unique to embryos in gymnosperms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===New definitions for embryonic plant cells and tissues=== | ||
| + | Both now have cross-product definitions, and no asserted is_a children | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[http://sourceforge.net/tracker/index.php?func=detail&aid=3177665&group_id=76834&atid=835555 embryonic plant cell]''' (PO:0025028): A plant cell that is part of a plant embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | -is_a embryonic plant structure, intersection_of: is_a plant cell, intersection_of: part_of embryo | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''embryonic apical cell''' (PO:0030007; replaces apical cell PO:0004000): An embryonic plant cell that is the uppermost cell formed after the first division of a zygote. | ||
| + | |||
| + | -is_a apical cell; part_of plant embryo (still dev_from zygote). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''embryonic basal cell''' (formerly: basal cell) (PO:0002002): An embryonic plant cell that is the lower-most cell formed after the first division of a zygote. | ||
| + | |||
| + | -is_a plant cell, part of plant embryo (still dev_from zygote) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''embryonic hypophysis''' (formerly hypophysis) (PO:0020109): An embryonic plant cell that is the uppermost cell of the suspensor from which part of the root and root cap in a plant embryo of an angiosperm are derived. | ||
| + | |||
| + | -is_a plant cell, part_of plant embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Is it true that this is only in angiosperms? ''Need to check this.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Although we don't have classes for them yet, we could add terms for any cell that is part of an embryo. For example, 16-cell stage embryonic plant cell would be "A plant cell that is part of an embyro in the 16-cell stage." This would still be inferred to be is_a embryonic plant cell.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''[https://sourceforge.net/tracker/index.php?func=detail&aid=3293751&group_id=76834&atid=835555 portion of embryonic plant tissue]''' (PO:0025233): A portion of plant tissue that is part of a plant embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | is_a embryonic plant structure, intersection_of: is_a portion of plant tissue, intersection_of: part_of plant embryo | ||
| + | |||
| + | Should we add the '''portion of''' prefix to the name? ''Yes'' | ||
| + | |||
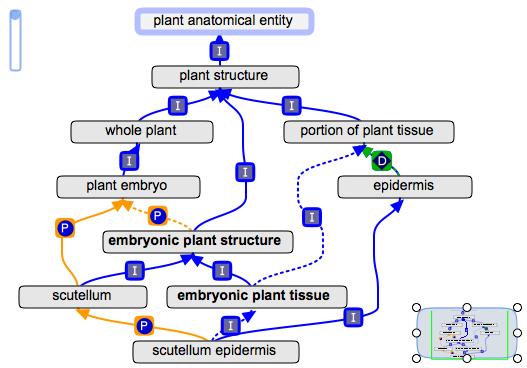
| + | * embryo cortex (PO:0005014), embryo endodermis (PO:0005015), embryonic shoot apical meristem (PO:0006362), epiblast (PO:0020036), scutellar epithelium (PO:0008048), and scutellum epidermis (PO:0006049) are now inferred children of (portion of) embryonic plant tissue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Here is a picture of some plant tissues, to show how it works: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Embryonic plant structure2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Definitions of embryonic plant cell and portion of embryonic plant tissue were accepted.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Proposed changes for structures that were is_a embryonic plant structure:=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====structures that only occur in embryos==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''embryo axis''' (PO:0019018): An axial part of an embryo that has as parts a hypocotyl and a root meristem or, if present, a radicle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Proposed definition:''' A plant axis that is the axial part of an embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Comment: Has a hypocotyl, root meristem, and radicle as parts, if present. | ||
| + | |||
| + | is_a plant axis, part_of embryo | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Should add zygotic embryo axis as a narrow synonym.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''plumule'''(PO:0020032): A somewhat differentiated terminal bud above the cotyledonary node, in which one or more internodes and leaves or scales can be discerned in a primordial stage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Comment: Occurs in several embryo types. | ||
| + | |||
| + | made is_a terminal bud, part_of embryo | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''embryonic leaf''' (PO:0006338): One of the first few leaves to develop from the embryonic shoot apical meristem [GR:pj]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Proposed definition:''' A vascular leaf that is part of an embryo and is one of the first few leaves to develop from the embryonic shoot apical meristem. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Comment: This term is used to described not yet fully-developed leaves that are part of an embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | is_a vascular leaf, part_of embryo | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''scutellar node''' (PO:0004708): The region in of an embryo axis between the primary root (enclosed in the coleorhiza) and the plumule (enclosed in the coleoptile) to which the scutellum is attached. [MaizeGDB:lv] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Too vague, because the region between the primary root and the plumule contains the mesocotyl as well as the scutellar node. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Proposed definition:''' A stem node that is the part of an embryo axis directly above the radicle where the scutellum is attached. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Comment: Found in grasses where no hypocotyl is present. The scutellar node may represent a reduction of the hypocotyl and cotyledonary node. [ref.: Esau 1965] | ||
| + | |||
| + | is_a stem node, part_of embryo axis | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''The changes described above were accepted.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====structures that occur in embryos and after embyronic phase==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''coleoptile''' (PO:0020033): A tubular (embryonic) plant structure developed at the junction of the cotyledonary sheath with the seedling axis, and surrounding the plumule of a monocot embryo or seedling. [APWeb:Glossary] | ||
| + | |||
| + | We do not have the term cotyledonary sheath in the PO, and, according to Beentje (the Kew Plant Glossary), the coleoptile ''is'' the cotyledonary sheath. Also, the coleoptile persists after germination, so it is not an embryonic plant structure. According to Esau, the coleoptile has stomata, which means it has an epidermis, and this consists of two or more tissue types. This makes it a plant organ, even though many authors casually refer to it as a tissue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Proposed definition:''' A phyllome that surrounds the plumule of an embryo or the emerging shoot apex of a seedling. [ISBN:9781842464229, ISBN: 0471244554] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Comment: Found in Poaceae. Develops at the first node above the scutellum, and thus is often thought to be the first leaf. Protects the emerging shoot system as it grows through the soil. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: A phyllome is "a lateral plant organ produced by a shoot apical meristem." | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''New children:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''embryonic coleoptile (PO:0025286)''': A coleoptile that is part of a plant embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''seedling coleoptile (PO:0025287)''': A coleoptile that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic coleoptile | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''It was suggested that we define the coleoptile as the first plastichron to form from the embryonic shoot apical meristem.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''RW after meeting: We don't have plastichron in the PO, and the term is generally used for measuring the age of plants based on the number of leaves produced. May be better to say it is the first phyllome formed.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''New proposed comment: Found in Poaceae. The coleoptile is the first phyllome formed from the embryonic shoot apical meristem. Protects the emerging shoot system as it grows through the soil.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''New definition for seedling coleoptile: A coleoptile that develops from an embryonic coleoptile. Comment: A seedling coleoptile is an elongation of an embryonic coleoptile and is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Use similar wording for other seedling structures.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''coleorhiza''' (PO:0020034): A portion of plant tissue surrounding the radicle in the embryo or seedling of some monocots. [APWeb:Glossary] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Currently part_of embryo, but it is also part of the seedling. It develops in the embryo, but persists after germination to protect the embryonic root. The coleorhiza, like the coleoptile, has an epidermis (and root hairs), and thus should be classified as a plant organ, even though many authors casually refer to it as a tissue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Proposed definition:''' A plant organ that surrounds the radicle in the embryo and seedling. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Comment: Found in Poaceae and some other monocots. Protects the emerging embryonic root. The parenchyma cells of both the coleorhiza and epiblast may function in storage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''New children:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''embryonic coleorhiza (PO:0025288)''': A coleorhiza that is part of a plant embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''seedling coleorhiza (PO:0025289)''': A coleorhiza that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic coleorhiza | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''hypocotyl''' (PO:0020100): The part of the stem below the cotyledonary node and transitional to a root, found in a young sporophyte. [APWeb:Glossary] | ||
| + | |||
| + | currently is_a cardinal organ part, propose is_a stem internode (we didn't have this term before but do now) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Proposed definition:''' A stem internode that is the part of a stem below the cotyledonary node and transitional to a root. | ||
| + | |||
| + | is_a stem internode | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''New children:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''embryonic hypocotyl (PO:0025290)''': A hypocotyl that is part of a plant embryo. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''seedling hypocotyl (PO:0025291)''': A hypocotyl that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic hypocotyl | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Some discussion of hypocotyl hook or apical hook. We already have the term PO:0000012 (apical hook, synonym hypocotyl hook), part_of hypocotyl. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''hypocotyl-root junction''' (PO:0004724): A cardinal organ part that is the part of a plant axis where a radicle joins a hypocotyl. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Moved to is_a cardinal organ part. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Proposed definition:''' A cardinal organ part that is the part of an embryonic axis where the radicle joins the hypocotyl. | ||
| + | |||
| + | synonym: embryo axis transition zone (Bell and Bryan 2008, and others) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''New children:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''embryonic hypocotyl-root junction (PO:0025300)''': A hypocotyl-root junction that is part of an embryo axis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''seedling hypocotyl-root junction (PO:0025301)''': A hypocotyl-root junction that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic hypocotyl-root junction | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Add Poaceae crown as narrow synonym of hypocotyl-root junction.'' | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | *'''epicotyl''' (PO:0020035): The first internode of a stem above the hypocotyl. In literature also used for the entire embryonic axis, consisting of several internodes, above the cotyledonary node. [APWeb:Glossary] | |
| − | + | currently is_a embryonic plant structure, propose is_a stem internode (PO:0005005). Also, the second part of the current definition only adds ambiguity. Need to define it more precisely. | |
| − | + | '''Proposed definition:''' The first stem internode above a hypocotyl. [Esau] | |
| − | + | Comment: The epicotyl is the first internode of a stem above the cotyledons. | |
| + | '''New children:''' | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''embryonic epicotyl (PO:0025292)''': A epicotyl that is part of a plant embryo. |
| − | + | '''seedling epicotyl (PO:0025293)''': A epicotyl that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase. | |
| + | (can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic epicotyl | ||
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | *'''mesocotyl''' (PO:0020037): The internode between the cotyledon or cotyledons and the leaf or leaves at the next node of a young sporophyte. |
| − | + | This definition sounds like the same thing as an epicotyl. Esau says the mesocotyl is the plant axis between the scutellum and the coleoptile and that in grasses, the scutellum is generally thought to represent the cotyledon and the coleoptile to represent the first leaf. In that case, the mesocotyl (as the axis between the scutellum and the coleoptile), is analogous (or homologous) to the epicotyl in dicots and other monocots. In grasses, the hypocotyl is not visible, except perhaps as the scutellar node. | |
| − | + | For a picture, see http://www.agry.purdue.edu/ext/corn/news/timeless/GerminationEvents.html | |
| − | + | '''Proposed definition:''' A shoot internode that is the part of an embryo axis or the stem of a seedling above the scutellum and below the coleoptile. [Easu] | |
| − | + | Comment: Occurs in grasses. In grasses, the hypocotyl and cotyledon may not be visible and may be represented by the scutellar node and scutellum, making the mesocotyl similar to the epicotyl in other taxa. Elongation of the mesocotyl during seedling growth pushes the coleoptile above the soil surface. | |
| − | + | '''New children:''' | |
| + | '''embryonic mesocotyl (PO:0025294)''': A mesocotyl that is part of a plant embryo. | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''seedling mesocotyl (PO:0025295)''': A mesocotyl that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase. |
| − | ' | + | (can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic mesocotyl |
| − | |||
| − | + | *'''embryonic root''' (PO:0000045): A root that is initiated in a developing embryo. [TAIR:ki] | |
| − | + | Embryonic root is not part_of embryo (at present). Has children '''radicle''' (PO:0020031) and '''seminal root''' (PO:0000046). | |
| − | + | Will need to revisit this when we look at organization of root (PO:0009005) | |
| − | |||
| − | + | *'''radicle''' (PO:0020031): The radicle is the basal continuation of the hypocotyl in an embryo and gives rise to the root system of the adult plant; sometimes more or less abortive. is_a embryonic root [APWeb:Glossary] | |
| − | + | '''Proposed definition:''' An embryonic root that is the basal continuation of a hypocotyl in an embryo. | |
| − | + | Comment: May develop into the root system of an adult plant. Sometimes abortive. | |
| − | + | Primary root (PO:0020127) develops from radicle. | |
| − | + | '''New children:''' | |
| − | + | '''embryonic radicle (PO:0025296)''': A radicle that is part of a plant embryo. | |
| − | + | '''seedling radicle (PO:0025297)''': A radicle that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase. | |
| − | + | (can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic radicle | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Except as noted above, the above definitions were accepted. Will reword the definitions of all of the seedling terms to reflect that they develop from the embryonic structures and post on Source Forge'' | |
| − | + | =New terms for Physcomitrella and related taxa (continued)= | |
| − | + | ==Collective plant structures:== | |
| − | + | ===[https://sourceforge.net/tracker/?func=detail&aid=3185093&group_id=76834&atid=835555 gametophore (PO:0030018)]=== | |
| − | + | Definition supplied by Moss Ontology: The leafy moss plant. The gametophore is the adult form of the moss gametophyte and bearer of the sex organs (gametangia). Ref: Reski (1998): Development, genetics and molecular biology of mosses. Botanica Acta 111, 1-15. | |
| − | + | Suggest is_a shoot system. | |
| − | + | '''Proposed def.:''' A shoot system that consists of the shoot axes and non-vascular leaves of a plant in the gametophytic phase. | |
| − | + | participates_in gametophytic phase, develops_from gametophore bud | |
| − | + | Comment: A gametophore is the leafy part of the gametophyte of mosses and leafy liverworts, excluding the protonema. Develop from buds that form on the protonema. Antheridia and archegonia arise on the gametophore. | |
| − | + | subset for bryophytes | |
| − | + | ''Accepted'' | |
| − | + | ===[https://sourceforge.net/tracker/?func=detail&aid=3185097&group_id=76834&atid=835555 gametophore bud (PO:0030026)]=== | |
| − | ' | + | The term "bud" has been requested: |
| + | Def'n supplied by Moss Ontology: A structure produced by a caulonema and able to develop into a gametophore or a stem that includes an apical cell able to develop into a gametophore. The earliest recognizable stage of gametophore development. Ref: Bill and Nancy Malcolm (2006): Mosses and other Bryophytes, an illustrated glossary, second edition and altered by David Cove | ||
| + | Suggest a new term '''gametophore bud'''. This could be a child of bud (PO:0000055: An undeveloped shoot system). | ||
| + | '''Proposed def'n:''' A vegetative bud that develops into a gametophore. | ||
| − | + | Comment: Occurs in mosses and leafy liverworts. Develops from a caulonema cell in mosses. | |
| − | + | participates_in gametophytic phase, has_part gametophore apical cell | |
| − | + | synonym: brown bud | |
| − | + | ''Accepted'' | |
| + | ===[https://sourceforge.net/tracker/?func=detail&aid=3257063&group_id=76834&atid=835555 thallus (PO:0030027)]=== | ||
| − | + | From Parihar: A simple vegetative plant body not differentiated into root, stem and leaf, and lacking vascular tissues. | |
| − | + | From Schofeld: A flattened gametophore in which no leaf-like organs dominate the structure. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Saying a thallus is a gametophore implies that it is a shoot system and therefore a collective plant structure (CPS). As a CPS, it must have more that one organ. This is not true for a thallus (sometime they branch, so you could say they have multiple axes, but it is a stretch. Maybe better to classify it as a whole plant. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''proposed def:''' A whole plant in the gametophytic phase that has a flat growth form and no distinct organs. | |
| − | + | Comment: A thallus is a gametophyte of liverworts and pteridophytes and develops from a short-lived protonema. Roughly two dimensional growth results from division of a single apical cell. Thalli may be ribbon or heart shaped or almost filamentous. Although there are no distinct organs, there may be tissue differentiation and dichotomous branching. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Add '''prothallium''' as a broad synonym of thallus and as a narrow synonym of whole plant. | |
| − | + | ''Accepted'' | |
| − | === | + | ===Other gametophyte terms=== |
| − | + | We need to keep in mind terms for other types of gametophytes, such as the subterranean, heterotrophic gametophytes of some ferns. RW, DWS, and MAG will maintain a list of terms that we don't need to add yet, but may want to add as time allows or need demands. Can use this list, for example, for writing a renewal of things that still need to be done. | |
| − | === | + | ==[https://sourceforge.net/tracker/?func=detail&aid=3234956&group_id=76834&atid=835555 apical cell]== |
| − | + | Moss Ontology has requested the term '''apical cell'''. Apical growth in byrophytes is via division of a single cell at the tip of the shoot apical meristem. They also requested '''shoot apical cell''' and '''phyllid apical cell'''. | |
| − | + | Non-seed vascular plants can also have an apical cell, that is, a single dividing cell at the apex of a root or shoot. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | We already have the term '''apical cell (PO:0004000)''', which is an embryonic cell: "An embryonic plant cell that is the uppermost cell formed after the first division of the zygote." The embryonic apical cell can also be found in non-angiosperms. Suggest obsoleting PO:0004000 and replacing it with the new term '''embryonic apical cell''' for clarity, and using the name '''apical cell''' for the general class of apical cells described below. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Definition of apical cell from Esau:''' The single initial cell in an apical meristem of root or shoot. Characteristic of many lower vascular plants. | |
| − | + | '''Definition of apical cell from Crum:''' A single cell at the tip of a stem, leaf, leaf or other structure that divides repeatedly to form new cells; also known as an apical intial. | |
| − | + | Is apical cell more consistent with '''meristematic cell''' (A cell synthesizing protoplasm and producing new cells by division and with only a primary cell wall) or with '''initial cell''' (A meristematic cell that by division gives rise to two cells, one of which remains meristematic, while the other is added to the plant body)? Probably meristematic cell, because the apical cell can give rise to more than two cells (because it can have three or four cutting faces). | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Proposed def. of apical cell (PO:0030007):''' A single meristematic cell at the tip of a shoot axis apex, leaf apex, root apex, or thallus apex. | |
| − | + | Comment: Occurs in bryophytes and some pteridophytes, where apical growth results from division of a single meristematic cell located at the tip of an apical meristem or plant organ, rather than from a population of meristematic cells located at the tip of an apical meristem. May be tetrahedral shaped, with three (in shoots) or four (in roots) cutting faces, or wedge shaped with two cutting faces (in non-vascular leaves or thalli). An apical cell may be established upon germination of a spore or upon the first cell division of an embryo or later. | |
| − | + | -note: the last sentence of the comment allows us to classify an embryonic apical cell as an apical cell. | |
| − | + | ''There was some discussion of whether or not apical cell should be is_a initial cell. It is important that the definition make it clear that this is not just any meristematic cell that is part of a shoot apex, but that it is one specific cell. Should look at papers for gene expression in these cells and compare to expression in SAMs or RAMs of seed plants. Will review definition at next meeting.'' | |
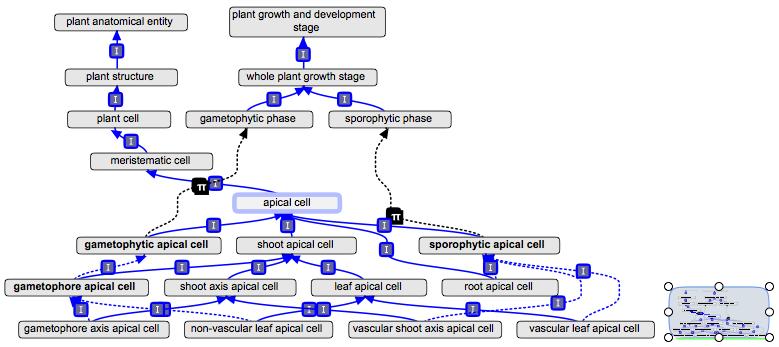
| − | + | Suggested ontology structure for the children of apical cell: | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:apical_cell1.jpg]] | |
| − | + | The dotted lines represent relations inferred by the reasoner. | |
| − | + | Includes two ways of classifying: by structure and by gametophyte/sporophyte. Structural relations are asserted as is_a relations. The relations to gametophyte or sporophyte are inferred by the intersection_of terms. | |
| + | ''This ontology structure was approved.'' | ||
| − | + | ''During the meeting PJ posted this link in the chat: [http://www.annualreviews.org/doi/full/10.1146/annurev.arplant.48.1.673 SAM Review] | |
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===New terms and definitions for apical cells=== |
| − | + | ''Definitions for the descendents of apical cell were approved, pending approval of final definition of apical cell.'' | |
| − | + | '''gametophytic apical cell (PO:0030014):''' An apical cell that is part of a whole plant in the gametophytic phase. | |
| − | + | Comment: Occurs bryophytes and pteridophytes. | |
| − | + | intersection_of: is_a apical cell, intersection_of: participates_in gametophytic phase | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''sporophytic apical cell (PO:0030015):''' An apical cell that is part of a whole plant in the sporophytic phase. | |
| − | + | Comment: Occurs in pteridophytes and the sporophyte of bryophytes. | |
| − | + | intersection_of: is_a apical cell, intersection_of: participates_in sporophytic phase | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''thallus apical cell (PO:0030025):''' An apical cell that is part of a thallus. | |
| − | + | part_of thallus | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''root apical cell (PO:0030008)''': A sporophytic apical cell that is part of a root apical meristem. | |
| − | + | comment: Occurs in the sporophytic phase of pteridophytes. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | part_of root apical meristem | |
| − | + | '''shoot apical cell (PO:0030009)''': An apical cell that is part of a shoot system. | |
| − | + | comment: May occur in shoot axes or leaves of bryophytes or ferns. | |
| − | + | part_of shoot system | |
| − | + | '''gametophore apical cell (PO:0030019)''': A shoot apical cell that is part of a gametophore. | |
| − | + | comment: Occurs in the non-vascular shoot system of the gametophyte of mosses and leafy liverworts. | |
| + | intersection_of: is_a shoot apical cell, intersection_of: part_of gametophore | ||
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''leaf apical cell (PO:0030011)''': A shoot apical cell that is part of a leaf apex. |
| − | + | comment: Occurs in the non-vascular leaves of bryophytes and the vascular leaves of some ferns. Only in plants where leaf growth is apical. | |
| + | part_of leaf apex | ||
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''non-vascular leaf apical cell (PO:0030013)''': A leaf apical cell that is part of a leaf apex of a non-vascular leaf. |
| + | comment: Occurs in the non-vascular leaves of bryophytes, which grow by division of a single, wedge-shaped apical cell with two cutting faces. | ||
| − | + | part_of non-vasucular leaf; synonym: phyllid apical cell | |
| − | |||
| − | ''' | + | '''vascular leaf apical cell (PO:0030012)''': A leaf apical cell that is part of the leaf apex of a vascular leaf. |
| − | + | comment: Occurs in vascular leaves of some ferns in their sporophytic phase. | |
| + | part_of vascular leaf | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''shoot axis apical cell (PO:0030010):''' An apical cell at the tip of a shoot apical meristem. | |
| + | Comment: Divides to produces leaf initial cells (if leaves are present) and other stem or branch tissues. | ||
| − | + | part_of shoot apical meristem | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''gametophore axis apical cell (PO:0030023)''': A shoot axis apical cell at the tip of a gametophore axis. | |
| − | + | Comment: Occurs at the tips of the stems and branches of bryophytes. | |
| − | + | part_of gametophore axis; synonym: cauloid apical cell, non-vascular shoot axis apical cell | |
| − | |||
| + | '''vascular shoot axis apical cell (PO:0030024)''': A shoot axis apical cell at the tip of a shoot apical meristem in a shoot system that has as part vascular tissue. | ||
| − | + | Comment: Occurs in some ferns in their sporophytic phase. | |
| − | + | participates_in sporophytic phase; synonym: fern shoot axis apical cell | |
| − | |||
| − | + | '''seta apical cell (PO:0030016)''': A shoot axis apical cell at the tip of a seta. | |
| − | + | Comment: Ceases being an apical cell when the sporangium begins to develop. | |
| + | part_of seta | ||
| − | + | Also: | |
| − | + | '''embryonic apical cell (PO:0025284, replaces PO:0004000)''': An apical cell that is part of a plant embryo and is the uppermost cell formed after the first division of a zygote. | |
| − | + | Comment: For plants that grow via an apical cell in their sporophytic phase, the embryonic apical cell may remain meristematic throughout the plant's life. | |
| + | =Review for OBO Foundry Acceptance= | ||
| + | At last weeks meeting, BS suggested that the PO can be submitted for OBO Foundry membership within the next weeks | ||
| − | [ | + | By email after the call: BS sent us a link to the list of principles: [[http://www.obofoundry.org/wiki/index.php/OBO_Foundry_Principles OBO_Foundry_Principles]] and then CM sent:"Use the list here": [[http://www.obofoundry.org/wiki/index.php/Category:Accepted Accepted]] |
| − | + | Which one is the one to use? | |
| − | + | =Upcoming meetings 2011:= | |
| + | '''[http://www.iplantcollaborative.org/2011/02/09/2011-semantic-web-workshop-june-6-7-santa-fe-nm 2011 Semantic Web Workshop] June 6th and 7th, Santa Fe, NM. | ||
| + | ''' | ||
| − | + | Hosted by Damian Gessler and the iPlant Collaborative, this two-day workshop will focus on biological applications for semantic web services. | |
| − | + | -JE and JP will be attending | |
| + | -JE has already worked with Damian to implement a SSWAP web service for PO terms, so further collaboration with him and iPlant will benefit the POC going forward. | ||
| − | [ | + | For more Workshop details: [http://www.iplantcollaborative.org/Communities/Developers/SemanticWeb Semantic web]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''* ICBO 2011 Second International Conference on Biomedical Ontology''' | |
| + | July 26-30, 2011 | ||
| + | Buffalo, New York | ||
| − | + | [http://icbo.buffalo.edu ICBO] | |
| + | LC is co-organizing the workshop "From Fins to Limbs to Leaves: Facilitating anatomy ontology interoperability" | ||
| + | along with Melissa Haendel, Chris Mungall, Alan Ruttenberg, David Osumi-Sutherland. | ||
| − | + | '''Full-Day Workshops Schedule:''' | |
| − | + | '''July 26 9am-6pm''' The Ontological Representation of Adverse Events: Working with Multiple Biomedical Ontologies | |
| − | + | '''July 27 8.30am-4pm''' Facilitating Anatomy Ontology Interoperability | |
| − | + | '''July 26 6.30pm-9pm''' Evening Workshop: Common Logic | |
| − | + | '''July 27 4pm-8pm''' Evening Workshop: Doctoral and Post-Doctoral Consortium | |
| − | + | - LC will attend and represent the PO. Invite other plant people? | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''*Plant Biology 2011, Aug 6-10th, Minneapolis, Minn''' | |
| − | + | [http://my.aspb.org/?page=Meetings_Annual Plant Biology 2011] | |
| − | + | Early-bird [http://www.aspb.org/meetings/pb-2011/registration.cfm registration] ends May 13. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Gramene will be putting together a workshop again, focusing on pathways. PJ will present a PO poster. | |
| − | + | TAIR (Kate Dreher) is organizing an Outreach Booth and we are invited to take part. | |
| − | + | For inclusion on the program memory stick and in the program book, abstracts must be submitted by '''May 27'''. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''* International Botanical Congress (IBC2011)''' | |
| − | - | + | July 23rd-30th 2011, Melbourne, Australia''' |
| − | + | Registration is open [http://www.ibc2011.com/Dates.htm Important dates] | |
| − | + | Symposium 'Bio-Ontologies for the Plant Sciences' under the Genetics, Genomics and Bioinformatics theme, wiil be held on Thursday, 27 July, from 13:30 to 15:30. | |
| − | + | Dennis, Alejandra, Pankaj and Ramona are planning to attend. | |
| − | + | See [[IBC 2011 Bio-Ontologies Symposium]] wiki page for more details | |
| − | =Next meeting scheduled for | + | =Next meeting scheduled for Thur, April 28th, 2011 at 10am PDT= |
Latest revision as of 13:19, 20 May 2011
POC meeting, Webex Conference Call; Date: Tuesday Apr 26th, 2011 10am (PDT)
In attendance:
POC members: Laurel Cooper (OSU), Ramona Walls (NYBG), Barry Smith (University at Buffalo, NY), Justin Preece (OSU), Justin Elser (OSU), ,Pankaj Jaiswal (OSU), Marie Alejandra Gandolfo (Cornell University)
Absent: Dennis Stevenson (NYBG), Chris Mungall (Lawrence Berkeley National Lab),
Collaborators: none
Acceptance of the minutes from the POC_Conf._Call_4-19-11? There were no changes, additions or deletions.
Summary of Plant Embryo and Embryonic Plant Structure Terms from last week's meeting:
plant embryo (PO:0009009)
Proposed new def'n: A whole plant in the early part of a sporophytic phase after the first cell division.
new proposed comment: An embryo is generally formed after the first division of a zygote, but in the case of adventitious embryos, somatic embryos, other embryos that arise through apogamy, and cultured haploid embryos, it is formed after the division of a single cell that is not a zygote. The end of the embryonic phase varies among taxa. In seed plants, the embryonic phase ends with germination. In pteridophytes, the embryonic phase ends with the formation of the first true leaf after the cotyledon(s). In bryophytes, the embryonic phase ends when the apical cell stops dividing and the sporangium begins to develop.
Add to comment: In cultured plant embryos, the embryonic phase ends when organs (roots, shoot axes, or leaves) begin to form.
* zygotic plant embryo (new term): proposed def'n: A plant embryo that forms as a result of the fusion of gametes. is_a plant embryo
* cultured zygote-derived plant embryo(new term): proposed def'n: A zygotic plant embryo that is grown or maintained in culture. synonym: cultured zygotic embryo, is_a zygotic (plant) embryo, and is_a cultured embryo
*microspore-derived cultured plant embryo (new term): proposed def'n: A cultured plant embryo that develops from isolated microspores.
is_a cultured plant embryo, synonym: microspore-derived haploid embryo
*somatic plant embryo (new term): proposed def'n: A plant embryo that forms as a result of apogamy.
Comment: Somatic plant embryo may arise where embryos normally would not arise, i.e. on the edges of leaves on Kalanchoe or ferns,
synonym: adventitious embryo (merge into new term) alt id: PO:0004537
*Cultured somatic (plant) embryo (PO:0000011) def'n: A (plant) embryo arising from previously differentiated somatic cells in vitro, rather than from fused haploid gametes, i.e., zygote.
propose revised def'n: A somatic plant embryo arising from previously differentiated somatic cells and grown and maintained in vitro.
is_a somatic plant embryo and also a cultured plant embryo.
The above terms and definitions were accepted. Okay to merge adventitious embryo with somatic embryo, but LC will look at it again to make sure.
Need to look for a good examples of somatic plant embryo -- it may be that Kalanchoe does not form embryos before plantlets form, need to check.
From LC after the meeting:
According to George et al , 2008: "Somatic embryogenesis is a process whereby somatic cells differentiate into somatic embryos. Somatic embryos resemble zygotic embryos morphologically. They are bipolar and bear typical embryonic organs. However, they develop via a different pathway. Somatic embryogenesis occurs to a limited extent under natural conditions, within ovules (e.g., Paeonia) and more rarely on leaves (e.g. Asplenium and Kalanchoe)."
Further evidence of this was presented by Garces et al, 2007, where they showed that constitutive plantlet-forming species, like Kalanchoë daigremontiana, form plantlets by co-opting both organogenesis and embryogenesis programs into leaves. They present evidence of both morphological and gene expression (LEC1 expression ) similarities to the formation of zygotic embryos.
Another example is commonly seen in Citrus, where apomixis occurs - this is perhaps what the original definition of "adventitious embryo" was referring to. (Embryo derived directly from nucellus cells without involving embryo sac cells.) this may be better called "apomitic plant embryo" There is quite a detailed review by Koltunow, from 1993.
We may want to reconsider merging the adventitious embryo term into the somatic embryo and rather rename it and make it an is_a child of.
Cited Refs:
George, E.F., Hall, M.A., and DeKlerk, G.J. (2008). Somatic Embryogenesis. In, The background, Plant propagation by Tissue Culture. Springer SBS, Dordrecht, p. 335–354. (http://www.hos.ufl.edu/mooreweb/tissueculture/february%205/somatic%20embryogenesis.pdf)
Garcês, H. M. P., Champagne, C. E. M., Townsley, B. T., Park, S., Malhó, R., Pedroso, M. C., Harada, J. J., and Sinha, N. R. (2007). Evolution of asexual reproduction in leaves of the genus Kalanchoë. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104, 15578 -15583. (http://www.pnas.org/content/104/39/15578.full)
Koltunow, A. M. (1993). Apomixis: Embryo Sacs and Embryos Formed without Meiosis or Fertilization in Ovules. The Plant Cell Online, 5, 1425 -1437. (http://www.plantcell.org/content/5/10/1425.full.pdf)
During the meeting PJ posted this link in the chat: Yang and sent this by email File:20-growth and development-02-A.pdf
embryonic plant structures
At the POC_Conf._Call_4-19-11 we discussed how to deal with structures that are part of an embryo when the plant is in the embryonic phase but are also part of a plant after it passes out of the embryonic phase, like hypocotyl root junction or coleorhiza.
As a solution, we will specify sibling terms like embryonic radicle and seedling radicle, with the correct part_of or participates_in relations and develops from relations (e.g., seedling radicle develops_from embryonic radicle). Includes six classes (see below).
* embryonic plant structure (PO:0025099): Proposed def'n: A plant structure that is part of an embryo.
Comment: Includes plant structures that only occur in embryos (such as suspensor) as well as plant structures that are part of an embryo when a plant is in the embryonic phase (such as embryonic radicle).
Definition accepted, except should say "plant embryo" instead of "embryo".
Need to be sure to use "plant embryo" instead of "embryo" in all definitions of descendent terms.
If, at a later point, we add embryonic phase or specific embryonic phases like 8 cell stage or 16 cell stage, we could use participates_in relation to define embryonic structures. However, as we are now defining it, embryonic plant structures should only include structures that are part of an embryo, not structures that are outside the embryo but present during the embryonic phase (like endosperm).
Terms that are is_a children of embryonic plant structure:
embryo proper (PO:0000001): An embryonic plant structure that is the body of a developing embryo attached to the maternal tissue in an ovule by a suspensor.
scutellum (PO:0020110): An embryonic plant structure that is a more or less shield-shaped and absorptive portion of an embryo of Poaceae.
suspensor (PO:0020108): An embryonic plant structure at the base of an embryo that develops from an embryonic basal cell and connects an embryo proper to the wall of a megagametophyte.
From DWS: We can also use Singh's "Embryology of Gymnosperms" as a basic reference to create a list of terms that are unique to embryos in gymnosperms.
New definitions for embryonic plant cells and tissues
Both now have cross-product definitions, and no asserted is_a children
embryonic plant cell (PO:0025028): A plant cell that is part of a plant embryo.
-is_a embryonic plant structure, intersection_of: is_a plant cell, intersection_of: part_of embryo
- embryonic apical cell (PO:0030007; replaces apical cell PO:0004000): An embryonic plant cell that is the uppermost cell formed after the first division of a zygote.
-is_a apical cell; part_of plant embryo (still dev_from zygote).
- embryonic basal cell (formerly: basal cell) (PO:0002002): An embryonic plant cell that is the lower-most cell formed after the first division of a zygote.
-is_a plant cell, part of plant embryo (still dev_from zygote)
- embryonic hypophysis (formerly hypophysis) (PO:0020109): An embryonic plant cell that is the uppermost cell of the suspensor from which part of the root and root cap in a plant embryo of an angiosperm are derived.
-is_a plant cell, part_of plant embryo.
Is it true that this is only in angiosperms? Need to check this.
Although we don't have classes for them yet, we could add terms for any cell that is part of an embryo. For example, 16-cell stage embryonic plant cell would be "A plant cell that is part of an embyro in the 16-cell stage." This would still be inferred to be is_a embryonic plant cell.
- portion of embryonic plant tissue (PO:0025233): A portion of plant tissue that is part of a plant embryo.
is_a embryonic plant structure, intersection_of: is_a portion of plant tissue, intersection_of: part_of plant embryo
Should we add the portion of prefix to the name? Yes
- embryo cortex (PO:0005014), embryo endodermis (PO:0005015), embryonic shoot apical meristem (PO:0006362), epiblast (PO:0020036), scutellar epithelium (PO:0008048), and scutellum epidermis (PO:0006049) are now inferred children of (portion of) embryonic plant tissue.
Here is a picture of some plant tissues, to show how it works:
Definitions of embryonic plant cell and portion of embryonic plant tissue were accepted.
Proposed changes for structures that were is_a embryonic plant structure:
structures that only occur in embryos
- embryo axis (PO:0019018): An axial part of an embryo that has as parts a hypocotyl and a root meristem or, if present, a radicle.
Proposed definition: A plant axis that is the axial part of an embryo.
Comment: Has a hypocotyl, root meristem, and radicle as parts, if present.
is_a plant axis, part_of embryo
Should add zygotic embryo axis as a narrow synonym.
- plumule(PO:0020032): A somewhat differentiated terminal bud above the cotyledonary node, in which one or more internodes and leaves or scales can be discerned in a primordial stage.
Comment: Occurs in several embryo types.
made is_a terminal bud, part_of embryo
- embryonic leaf (PO:0006338): One of the first few leaves to develop from the embryonic shoot apical meristem [GR:pj].
Proposed definition: A vascular leaf that is part of an embryo and is one of the first few leaves to develop from the embryonic shoot apical meristem.
Comment: This term is used to described not yet fully-developed leaves that are part of an embryo.
is_a vascular leaf, part_of embryo
- scutellar node (PO:0004708): The region in of an embryo axis between the primary root (enclosed in the coleorhiza) and the plumule (enclosed in the coleoptile) to which the scutellum is attached. [MaizeGDB:lv]
Too vague, because the region between the primary root and the plumule contains the mesocotyl as well as the scutellar node.
Proposed definition: A stem node that is the part of an embryo axis directly above the radicle where the scutellum is attached.
Comment: Found in grasses where no hypocotyl is present. The scutellar node may represent a reduction of the hypocotyl and cotyledonary node. [ref.: Esau 1965]
is_a stem node, part_of embryo axis
The changes described above were accepted.
structures that occur in embryos and after embyronic phase
- coleoptile (PO:0020033): A tubular (embryonic) plant structure developed at the junction of the cotyledonary sheath with the seedling axis, and surrounding the plumule of a monocot embryo or seedling. [APWeb:Glossary]
We do not have the term cotyledonary sheath in the PO, and, according to Beentje (the Kew Plant Glossary), the coleoptile is the cotyledonary sheath. Also, the coleoptile persists after germination, so it is not an embryonic plant structure. According to Esau, the coleoptile has stomata, which means it has an epidermis, and this consists of two or more tissue types. This makes it a plant organ, even though many authors casually refer to it as a tissue.
Proposed definition: A phyllome that surrounds the plumule of an embryo or the emerging shoot apex of a seedling. [ISBN:9781842464229, ISBN: 0471244554]
Comment: Found in Poaceae. Develops at the first node above the scutellum, and thus is often thought to be the first leaf. Protects the emerging shoot system as it grows through the soil.
Note: A phyllome is "a lateral plant organ produced by a shoot apical meristem."
New children:
embryonic coleoptile (PO:0025286): A coleoptile that is part of a plant embryo.
seedling coleoptile (PO:0025287): A coleoptile that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.
(can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic coleoptile
It was suggested that we define the coleoptile as the first plastichron to form from the embryonic shoot apical meristem.
RW after meeting: We don't have plastichron in the PO, and the term is generally used for measuring the age of plants based on the number of leaves produced. May be better to say it is the first phyllome formed.
New proposed comment: Found in Poaceae. The coleoptile is the first phyllome formed from the embryonic shoot apical meristem. Protects the emerging shoot system as it grows through the soil.
New definition for seedling coleoptile: A coleoptile that develops from an embryonic coleoptile. Comment: A seedling coleoptile is an elongation of an embryonic coleoptile and is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.
Use similar wording for other seedling structures.
- coleorhiza (PO:0020034): A portion of plant tissue surrounding the radicle in the embryo or seedling of some monocots. [APWeb:Glossary]
Currently part_of embryo, but it is also part of the seedling. It develops in the embryo, but persists after germination to protect the embryonic root. The coleorhiza, like the coleoptile, has an epidermis (and root hairs), and thus should be classified as a plant organ, even though many authors casually refer to it as a tissue.
Proposed definition: A plant organ that surrounds the radicle in the embryo and seedling.
Comment: Found in Poaceae and some other monocots. Protects the emerging embryonic root. The parenchyma cells of both the coleorhiza and epiblast may function in storage.
New children:
embryonic coleorhiza (PO:0025288): A coleorhiza that is part of a plant embryo.
seedling coleorhiza (PO:0025289): A coleorhiza that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.
(can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic coleorhiza
- hypocotyl (PO:0020100): The part of the stem below the cotyledonary node and transitional to a root, found in a young sporophyte. [APWeb:Glossary]
currently is_a cardinal organ part, propose is_a stem internode (we didn't have this term before but do now)
Proposed definition: A stem internode that is the part of a stem below the cotyledonary node and transitional to a root.
is_a stem internode
New children:
embryonic hypocotyl (PO:0025290): A hypocotyl that is part of a plant embryo.
seedling hypocotyl (PO:0025291): A hypocotyl that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.
(can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic hypocotyl
Some discussion of hypocotyl hook or apical hook. We already have the term PO:0000012 (apical hook, synonym hypocotyl hook), part_of hypocotyl.
- hypocotyl-root junction (PO:0004724): A cardinal organ part that is the part of a plant axis where a radicle joins a hypocotyl.
Moved to is_a cardinal organ part.
Proposed definition: A cardinal organ part that is the part of an embryonic axis where the radicle joins the hypocotyl.
synonym: embryo axis transition zone (Bell and Bryan 2008, and others)
New children:
embryonic hypocotyl-root junction (PO:0025300): A hypocotyl-root junction that is part of an embryo axis.
seedling hypocotyl-root junction (PO:0025301): A hypocotyl-root junction that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.
(can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic hypocotyl-root junction
Add Poaceae crown as narrow synonym of hypocotyl-root junction.
- epicotyl (PO:0020035): The first internode of a stem above the hypocotyl. In literature also used for the entire embryonic axis, consisting of several internodes, above the cotyledonary node. [APWeb:Glossary]
currently is_a embryonic plant structure, propose is_a stem internode (PO:0005005). Also, the second part of the current definition only adds ambiguity. Need to define it more precisely.
Proposed definition: The first stem internode above a hypocotyl. [Esau]
Comment: The epicotyl is the first internode of a stem above the cotyledons.
New children:
embryonic epicotyl (PO:0025292): A epicotyl that is part of a plant embryo.
seedling epicotyl (PO:0025293): A epicotyl that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.
(can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic epicotyl
- mesocotyl (PO:0020037): The internode between the cotyledon or cotyledons and the leaf or leaves at the next node of a young sporophyte.
This definition sounds like the same thing as an epicotyl. Esau says the mesocotyl is the plant axis between the scutellum and the coleoptile and that in grasses, the scutellum is generally thought to represent the cotyledon and the coleoptile to represent the first leaf. In that case, the mesocotyl (as the axis between the scutellum and the coleoptile), is analogous (or homologous) to the epicotyl in dicots and other monocots. In grasses, the hypocotyl is not visible, except perhaps as the scutellar node.
For a picture, see http://www.agry.purdue.edu/ext/corn/news/timeless/GerminationEvents.html
Proposed definition: A shoot internode that is the part of an embryo axis or the stem of a seedling above the scutellum and below the coleoptile. [Easu]
Comment: Occurs in grasses. In grasses, the hypocotyl and cotyledon may not be visible and may be represented by the scutellar node and scutellum, making the mesocotyl similar to the epicotyl in other taxa. Elongation of the mesocotyl during seedling growth pushes the coleoptile above the soil surface.
New children:
embryonic mesocotyl (PO:0025294): A mesocotyl that is part of a plant embryo.
seedling mesocotyl (PO:0025295): A mesocotyl that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.
(can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic mesocotyl
- embryonic root (PO:0000045): A root that is initiated in a developing embryo. [TAIR:ki]
Embryonic root is not part_of embryo (at present). Has children radicle (PO:0020031) and seminal root (PO:0000046).
Will need to revisit this when we look at organization of root (PO:0009005)
- radicle (PO:0020031): The radicle is the basal continuation of the hypocotyl in an embryo and gives rise to the root system of the adult plant; sometimes more or less abortive. is_a embryonic root [APWeb:Glossary]
Proposed definition: An embryonic root that is the basal continuation of a hypocotyl in an embryo.
Comment: May develop into the root system of an adult plant. Sometimes abortive.
Primary root (PO:0020127) develops from radicle.
New children:
embryonic radicle (PO:0025296): A radicle that is part of a plant embryo.
seedling radicle (PO:0025297): A radicle that is part of a whole plant in the seedling phase.
(can't add participates in seedling phase yet) develops_from embryonic radicle
Except as noted above, the above definitions were accepted. Will reword the definitions of all of the seedling terms to reflect that they develop from the embryonic structures and post on Source Forge
Collective plant structures:
gametophore (PO:0030018)
Definition supplied by Moss Ontology: The leafy moss plant. The gametophore is the adult form of the moss gametophyte and bearer of the sex organs (gametangia). Ref: Reski (1998): Development, genetics and molecular biology of mosses. Botanica Acta 111, 1-15.
Suggest is_a shoot system.
Proposed def.: A shoot system that consists of the shoot axes and non-vascular leaves of a plant in the gametophytic phase.
participates_in gametophytic phase, develops_from gametophore bud
Comment: A gametophore is the leafy part of the gametophyte of mosses and leafy liverworts, excluding the protonema. Develop from buds that form on the protonema. Antheridia and archegonia arise on the gametophore.
subset for bryophytes
Accepted
gametophore bud (PO:0030026)
The term "bud" has been requested: Def'n supplied by Moss Ontology: A structure produced by a caulonema and able to develop into a gametophore or a stem that includes an apical cell able to develop into a gametophore. The earliest recognizable stage of gametophore development. Ref: Bill and Nancy Malcolm (2006): Mosses and other Bryophytes, an illustrated glossary, second edition and altered by David Cove
Suggest a new term gametophore bud. This could be a child of bud (PO:0000055: An undeveloped shoot system).
Proposed def'n: A vegetative bud that develops into a gametophore.
Comment: Occurs in mosses and leafy liverworts. Develops from a caulonema cell in mosses.
participates_in gametophytic phase, has_part gametophore apical cell
synonym: brown bud
Accepted
thallus (PO:0030027)
From Parihar: A simple vegetative plant body not differentiated into root, stem and leaf, and lacking vascular tissues.
From Schofeld: A flattened gametophore in which no leaf-like organs dominate the structure.
Saying a thallus is a gametophore implies that it is a shoot system and therefore a collective plant structure (CPS). As a CPS, it must have more that one organ. This is not true for a thallus (sometime they branch, so you could say they have multiple axes, but it is a stretch. Maybe better to classify it as a whole plant.
proposed def: A whole plant in the gametophytic phase that has a flat growth form and no distinct organs.
Comment: A thallus is a gametophyte of liverworts and pteridophytes and develops from a short-lived protonema. Roughly two dimensional growth results from division of a single apical cell. Thalli may be ribbon or heart shaped or almost filamentous. Although there are no distinct organs, there may be tissue differentiation and dichotomous branching.
Add prothallium as a broad synonym of thallus and as a narrow synonym of whole plant.
Accepted
Other gametophyte terms
We need to keep in mind terms for other types of gametophytes, such as the subterranean, heterotrophic gametophytes of some ferns. RW, DWS, and MAG will maintain a list of terms that we don't need to add yet, but may want to add as time allows or need demands. Can use this list, for example, for writing a renewal of things that still need to be done.
apical cell
Moss Ontology has requested the term apical cell. Apical growth in byrophytes is via division of a single cell at the tip of the shoot apical meristem. They also requested shoot apical cell and phyllid apical cell.
Non-seed vascular plants can also have an apical cell, that is, a single dividing cell at the apex of a root or shoot.
We already have the term apical cell (PO:0004000), which is an embryonic cell: "An embryonic plant cell that is the uppermost cell formed after the first division of the zygote." The embryonic apical cell can also be found in non-angiosperms. Suggest obsoleting PO:0004000 and replacing it with the new term embryonic apical cell for clarity, and using the name apical cell for the general class of apical cells described below.
Definition of apical cell from Esau: The single initial cell in an apical meristem of root or shoot. Characteristic of many lower vascular plants.
Definition of apical cell from Crum: A single cell at the tip of a stem, leaf, leaf or other structure that divides repeatedly to form new cells; also known as an apical intial.
Is apical cell more consistent with meristematic cell (A cell synthesizing protoplasm and producing new cells by division and with only a primary cell wall) or with initial cell (A meristematic cell that by division gives rise to two cells, one of which remains meristematic, while the other is added to the plant body)? Probably meristematic cell, because the apical cell can give rise to more than two cells (because it can have three or four cutting faces).
Proposed def. of apical cell (PO:0030007): A single meristematic cell at the tip of a shoot axis apex, leaf apex, root apex, or thallus apex.
Comment: Occurs in bryophytes and some pteridophytes, where apical growth results from division of a single meristematic cell located at the tip of an apical meristem or plant organ, rather than from a population of meristematic cells located at the tip of an apical meristem. May be tetrahedral shaped, with three (in shoots) or four (in roots) cutting faces, or wedge shaped with two cutting faces (in non-vascular leaves or thalli). An apical cell may be established upon germination of a spore or upon the first cell division of an embryo or later.
-note: the last sentence of the comment allows us to classify an embryonic apical cell as an apical cell.
There was some discussion of whether or not apical cell should be is_a initial cell. It is important that the definition make it clear that this is not just any meristematic cell that is part of a shoot apex, but that it is one specific cell. Should look at papers for gene expression in these cells and compare to expression in SAMs or RAMs of seed plants. Will review definition at next meeting.
Suggested ontology structure for the children of apical cell:
The dotted lines represent relations inferred by the reasoner.
Includes two ways of classifying: by structure and by gametophyte/sporophyte. Structural relations are asserted as is_a relations. The relations to gametophyte or sporophyte are inferred by the intersection_of terms.
This ontology structure was approved.
During the meeting PJ posted this link in the chat: SAM Review
New terms and definitions for apical cells
Definitions for the descendents of apical cell were approved, pending approval of final definition of apical cell.
gametophytic apical cell (PO:0030014): An apical cell that is part of a whole plant in the gametophytic phase.
Comment: Occurs bryophytes and pteridophytes.
intersection_of: is_a apical cell, intersection_of: participates_in gametophytic phase
sporophytic apical cell (PO:0030015): An apical cell that is part of a whole plant in the sporophytic phase.
Comment: Occurs in pteridophytes and the sporophyte of bryophytes.
intersection_of: is_a apical cell, intersection_of: participates_in sporophytic phase
thallus apical cell (PO:0030025): An apical cell that is part of a thallus.
part_of thallus
root apical cell (PO:0030008): A sporophytic apical cell that is part of a root apical meristem.
comment: Occurs in the sporophytic phase of pteridophytes.
part_of root apical meristem
shoot apical cell (PO:0030009): An apical cell that is part of a shoot system.
comment: May occur in shoot axes or leaves of bryophytes or ferns.
part_of shoot system
gametophore apical cell (PO:0030019): A shoot apical cell that is part of a gametophore.
comment: Occurs in the non-vascular shoot system of the gametophyte of mosses and leafy liverworts.
intersection_of: is_a shoot apical cell, intersection_of: part_of gametophore
leaf apical cell (PO:0030011): A shoot apical cell that is part of a leaf apex.
comment: Occurs in the non-vascular leaves of bryophytes and the vascular leaves of some ferns. Only in plants where leaf growth is apical.
part_of leaf apex
non-vascular leaf apical cell (PO:0030013): A leaf apical cell that is part of a leaf apex of a non-vascular leaf.
comment: Occurs in the non-vascular leaves of bryophytes, which grow by division of a single, wedge-shaped apical cell with two cutting faces.
part_of non-vasucular leaf; synonym: phyllid apical cell
vascular leaf apical cell (PO:0030012): A leaf apical cell that is part of the leaf apex of a vascular leaf.
comment: Occurs in vascular leaves of some ferns in their sporophytic phase.
part_of vascular leaf
shoot axis apical cell (PO:0030010): An apical cell at the tip of a shoot apical meristem.
Comment: Divides to produces leaf initial cells (if leaves are present) and other stem or branch tissues.
part_of shoot apical meristem
gametophore axis apical cell (PO:0030023): A shoot axis apical cell at the tip of a gametophore axis.
Comment: Occurs at the tips of the stems and branches of bryophytes.
part_of gametophore axis; synonym: cauloid apical cell, non-vascular shoot axis apical cell
vascular shoot axis apical cell (PO:0030024): A shoot axis apical cell at the tip of a shoot apical meristem in a shoot system that has as part vascular tissue.
Comment: Occurs in some ferns in their sporophytic phase.
participates_in sporophytic phase; synonym: fern shoot axis apical cell
seta apical cell (PO:0030016): A shoot axis apical cell at the tip of a seta.
Comment: Ceases being an apical cell when the sporangium begins to develop.
part_of seta
Also:
embryonic apical cell (PO:0025284, replaces PO:0004000): An apical cell that is part of a plant embryo and is the uppermost cell formed after the first division of a zygote.
Comment: For plants that grow via an apical cell in their sporophytic phase, the embryonic apical cell may remain meristematic throughout the plant's life.
Review for OBO Foundry Acceptance
At last weeks meeting, BS suggested that the PO can be submitted for OBO Foundry membership within the next weeks
By email after the call: BS sent us a link to the list of principles: [OBO_Foundry_Principles] and then CM sent:"Use the list here": [Accepted]
Which one is the one to use?
Upcoming meetings 2011:
2011 Semantic Web Workshop June 6th and 7th, Santa Fe, NM.
Hosted by Damian Gessler and the iPlant Collaborative, this two-day workshop will focus on biological applications for semantic web services.
-JE and JP will be attending
-JE has already worked with Damian to implement a SSWAP web service for PO terms, so further collaboration with him and iPlant will benefit the POC going forward.
For more Workshop details: Semantic web.
* ICBO 2011 Second International Conference on Biomedical Ontology
July 26-30, 2011
Buffalo, New York
LC is co-organizing the workshop "From Fins to Limbs to Leaves: Facilitating anatomy ontology interoperability" along with Melissa Haendel, Chris Mungall, Alan Ruttenberg, David Osumi-Sutherland.
Full-Day Workshops Schedule:
July 26 9am-6pm The Ontological Representation of Adverse Events: Working with Multiple Biomedical Ontologies
July 27 8.30am-4pm Facilitating Anatomy Ontology Interoperability
July 26 6.30pm-9pm Evening Workshop: Common Logic
July 27 4pm-8pm Evening Workshop: Doctoral and Post-Doctoral Consortium
- LC will attend and represent the PO. Invite other plant people?
*Plant Biology 2011, Aug 6-10th, Minneapolis, Minn
Early-bird registration ends May 13.
Gramene will be putting together a workshop again, focusing on pathways. PJ will present a PO poster.
TAIR (Kate Dreher) is organizing an Outreach Booth and we are invited to take part.
For inclusion on the program memory stick and in the program book, abstracts must be submitted by May 27.
* International Botanical Congress (IBC2011)
July 23rd-30th 2011, Melbourne, Australia
Registration is open Important dates
Symposium 'Bio-Ontologies for the Plant Sciences' under the Genetics, Genomics and Bioinformatics theme, wiil be held on Thursday, 27 July, from 13:30 to 15:30.
Dennis, Alejandra, Pankaj and Ramona are planning to attend.
See IBC 2011 Bio-Ontologies Symposium wiki page for more details